Configure the OpenShift cloud provider
You can configure OpenShift for YugabyteDB universes using YugabyteDB Anywhere. If no cloud providers are configured via YugabyteDB Anywhere, the main Dashboard page requests to configure at least one provider.
To create a YugabyteDB universe using the deployed YugabyteDB Anywhere, you start by creating the required role-based access control (RBAC) and adding the provider in the YugabyteDB Anywhere.
Create RBAC and kubeconfig
kubeconfig is used by YugabyteDB Anywhere to create universes in the OpenShift Container Platform (OCP) cluster.
To create a service account in the yb-platform project, execute the following command:
oc apply \
-n yb-platform \
-f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/yugabyte/charts/master/rbac/yugabyte-platform-universe-management-sa.yaml
Expect the following output:
serviceaccount/yugabyte-platform-universe-management created
The next step is to grant access to this service account using Roles and RoleBindings, thus allowing it to manage the YugabyteDB universe's resources for you. If you are creating clusters across multiple namespaces, you need to create Roles and RoleBindings with a cluster-admin role in each namespace where you intend to create and deploy the universe. For more information, see RBAC resources.
To create the required RBAC objects, execute the following command:
curl -s https://raw.githubusercontent.com/yugabyte/charts/master/rbac/platform-namespaced.yaml \
| sed "s/namespace: <SA_NAMESPACE>/namespace: yb-platform/g" \
| oc apply -n yb-platform -f -
Expect the following output:
role.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/yugabyte-helm-operations created
role.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/yugabyte-management created
rolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/yugabyte-helm-operations created
rolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/yugabyte-management created
The next step is to create a kubeconfig for this service account. You download a helper script for generating a kubeconfig file by executing the following command:
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/YugaByte/charts/master/stable/yugabyte/generate_kubeconfig.py
To generate the kubeconfig file, execute the following:
python generate_kubeconfig.py \
--service_account yugabyte-platform-universe-management \
--namespace yb-platform
Expect the following output:
Generated the kubeconfig file: /tmp/yugabyte-platform-universe-management.conf
Create a provider in YugabyteDB Anywhere
Since YugabyteDB Anywhere manages YugabyteDB universes, YugabyteDB Anywhere needs details about the cloud providers. In your case, the provider is your own OCP cluster.
You can create a provider as follows:
-
Open YugabyteDB Anywhere UI and click Configure a Provider to open the Cloud Provider Configuration page shown in the following illustration.
-
Select Red Hat OpenShift and complete the fields, as follows:
- In the Type filed, select OpenShift.
- In the Name field, enter ocp-test.
- Use the Kube Config field to select the file that you created in the preceding step.
- In the Service Account field, enter yugabyte-platform-universe-management.
- In the Image Registry field, if you are performing Operator-based installation, use
registry.connect.redhat.com/yugabytedb/yugabyte, and if you are performing Helm-based installation, usequay.io/yugabyte/yugabyte-ubi - Optionally, use the Pull Secret File field to upload the pull secret you received from Yugabyte Support.
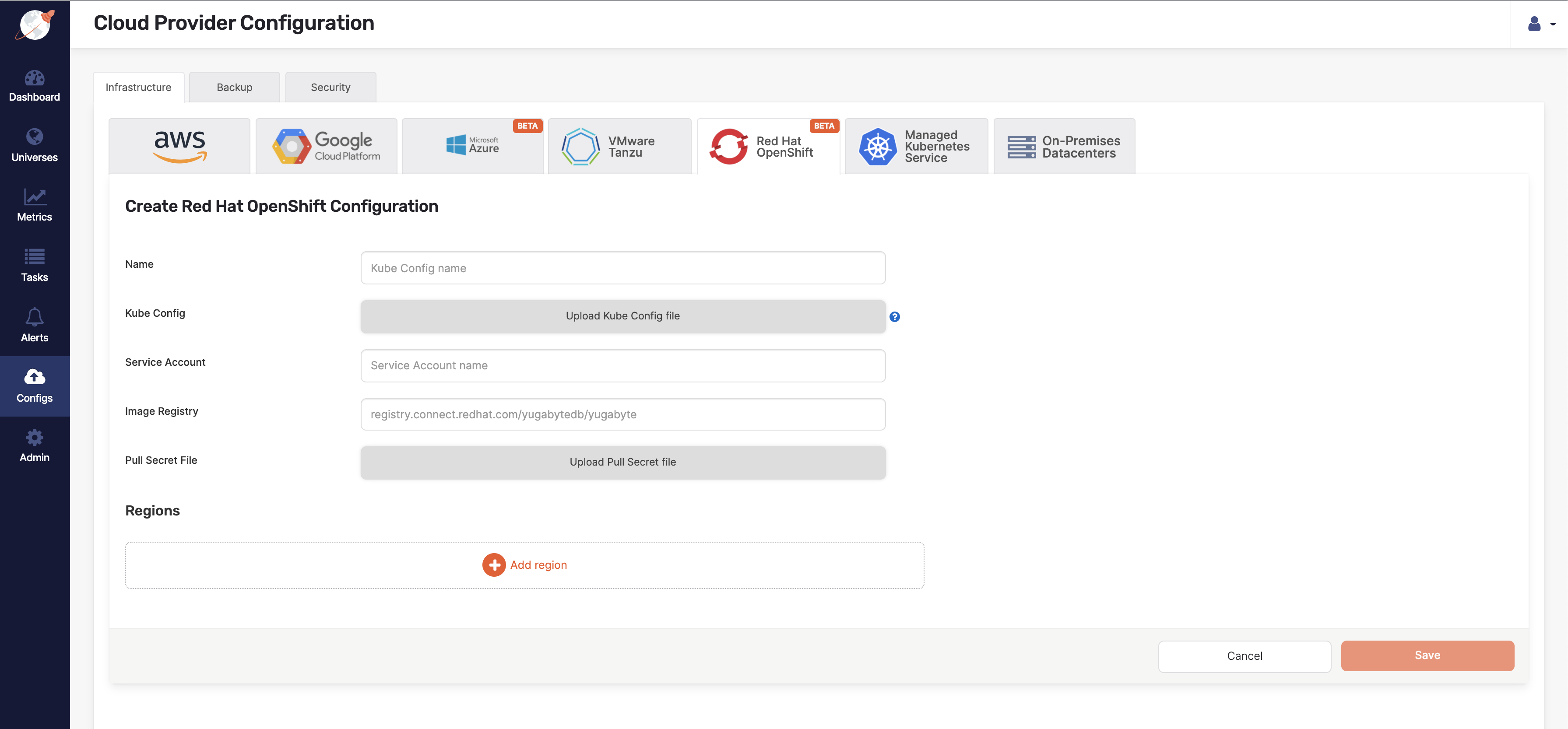
-
Click Add Region and complete the Add new region dialog shown in the following illustration by first selecting the region you found previously (US East), and then entering the following information:
- In the Zone field, enter the exact zone label (us-east4-a).
- In the Namespace field, enter yb-platform.
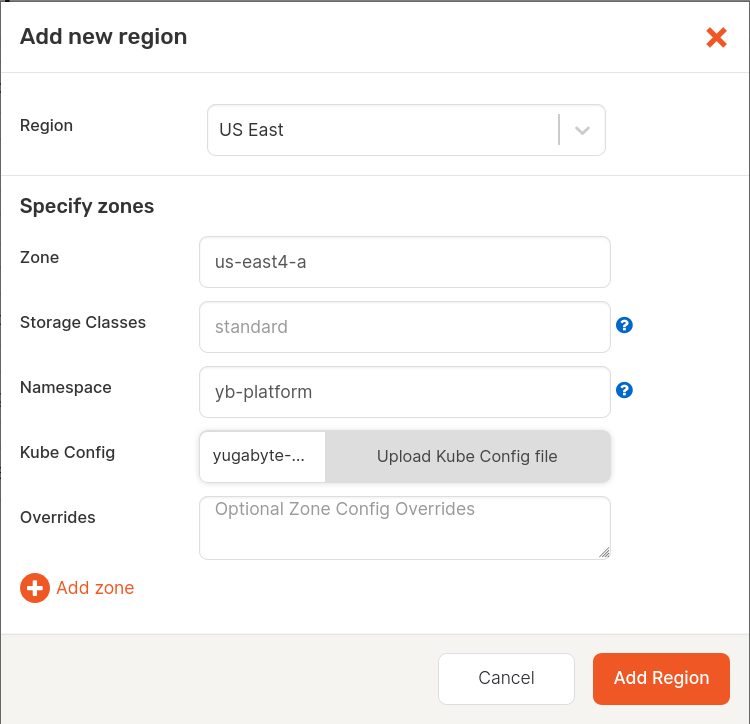
-
Click Add Region.
-
Click Save.
You should see the newly-added provider under Red Hat OpenShift configs.
Create a universe using the provider
You can create a universe using the provider as follows:
-
Use YugabyteDB Anywhere UI to navigate to Universes, and then click Create Universe.
-
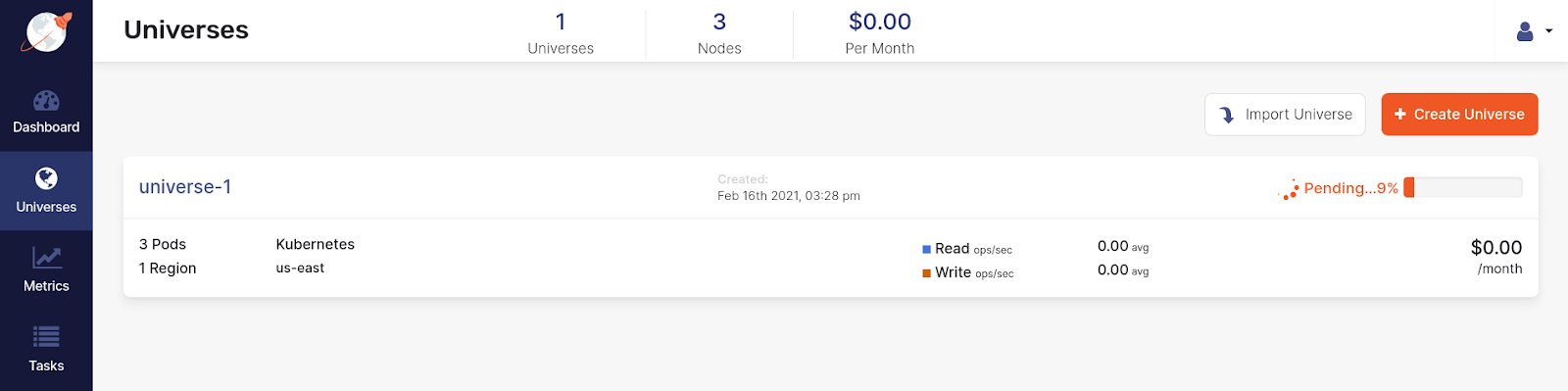
Complete the Create Universe page shown in the following illustration by entering the following information:
- In the Name field, enter universe-1.
- In the Provider field, enter ocp-test.
- In the Regions field, enter US East.
- In the Instance Type field, enter xsmall (2 cores, 4GB RAM).

-
Click Create.
The following illustration shows the universe creation progress:
If you click universe-1 and then navigate to Tasks, you should see a page similar to the one shown in the following illustration:

Upon successful creation of the universe, the Overview tab of universe-1 should look similar to the following:
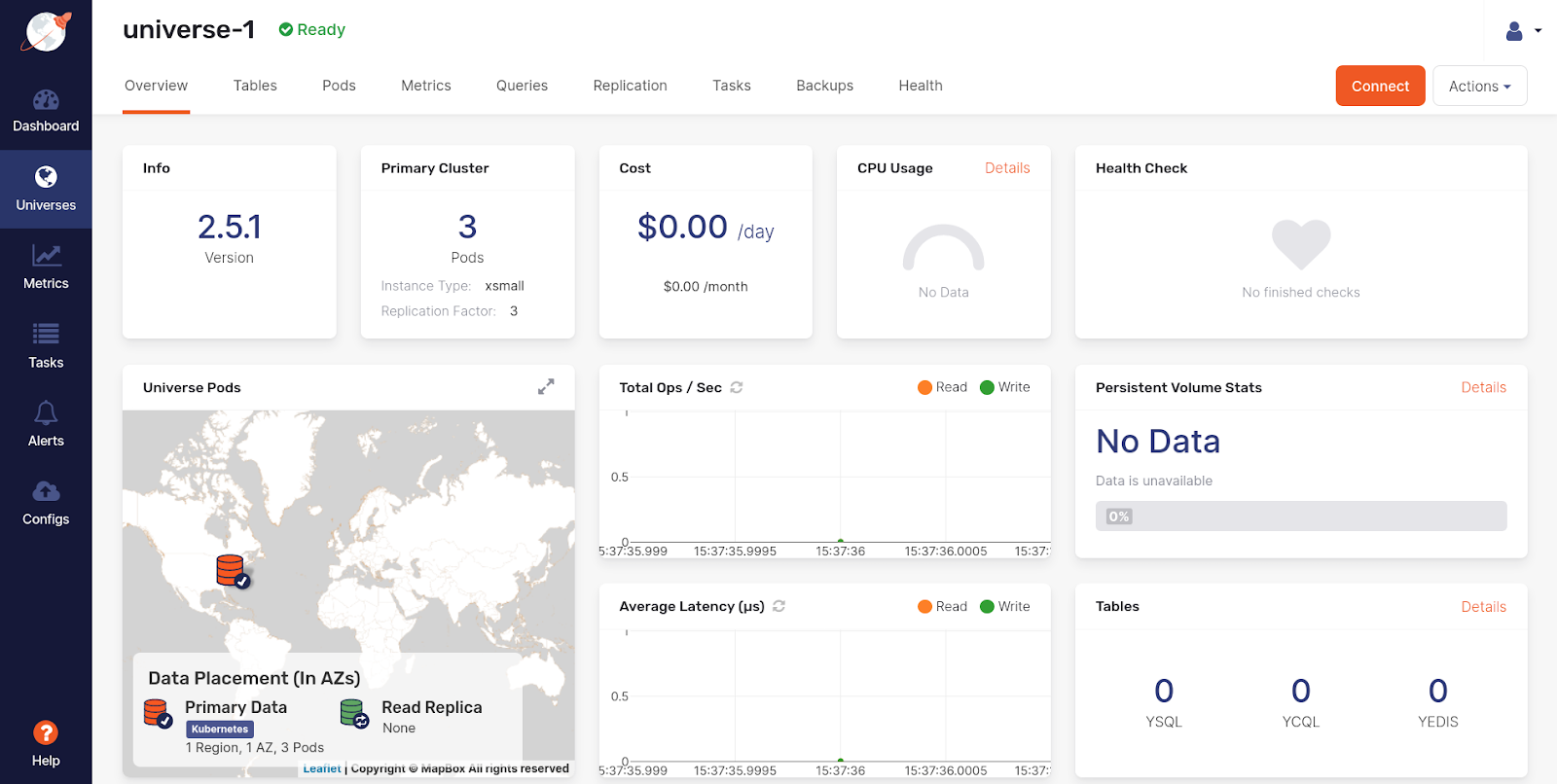
Troubleshoot the universe creation
If the universe creation remains in Pending state for more than 2-3 minutes, open the OCP web console, navigate to Workloads > Pods and check if any of the pods are in pending state, as shown in the following illustration:
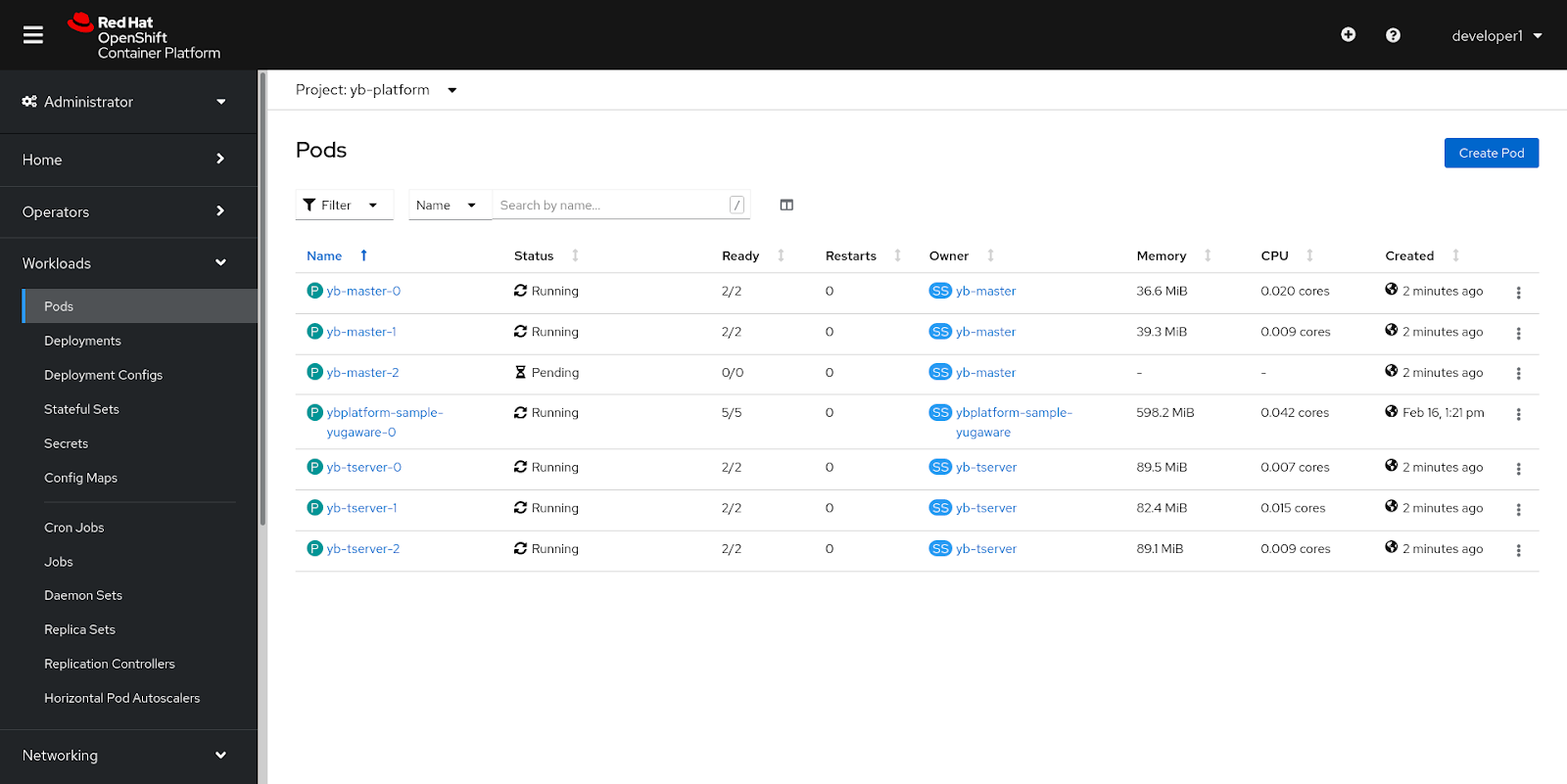
Alternatively, you can execute the following command to check status of the pods:
oc get pods -n yb-platform -l chart=yugabyte
Expect an output similar to the following:
# output
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
yb-master-0 2/2 Running 0 5m58s
yb-master-1 2/2 Running 0 5m58s
yb-master-2 0/2 Pending 0 5m58s
yb-tserver-0 2/2 Running 0 5m58s
yb-tserver-1 2/2 Running 0 5m58s
yb-tserver-2 2/2 Running 0 5m58s
If any of the pods are in pending state, perform the following:
- Login with an admin account and navigate to Compute > Machine Sets.
- Open the Machine Set corresponding to your zone label (us-east4-a).
- Click Desired Count and increase the count by 1 or 2, as shown in the following illustration.
- Click Save.

Alternatively, you can scale the Machine Sets by executing the following command as admin user:
oc scale machineset ocp-dev4-l5ffp-worker-a --replicas=2 -n openshift-machine-api
Expect the following output:
# output
machineset.machine.openshift.io/ocp-dev4-l5ffp-worker-a scaled
As soon as the new machine is added, the pending pods become ready.