Quick start
The quickest way to get started with YugabyteDB is to sign up for YugabyteDB Managed and create a free Sandbox cluster.
After setting up your YugabyteDB Managed account, log in to access YugabyteDB Managed.
The first time you sign in, YugabyteDB Managed provides a welcome experience with a 15 minute Get Started tutorial. Follow the steps to learn how to do the following:
- Create your Sandbox cluster
- Use YugabyteDB to create a database, load sample data, and run queries
- Explore a sample application that matches your use case
If you aren't using the Get Started tutorial, use the following instructions to create your first cluster and connect to your database.
Create your Sandbox cluster
The Sandbox cluster provides a fully functioning single node YugabyteDB cluster deployed to the region of your choice. The cluster is free forever and includes enough resources to explore the core features available for developing applications with YugabyteDB. No credit card information is required.
To create your Sandbox cluster:
-
Click Create a Free cluster on the welcome screen, or click Add Cluster on the Clusters page to open the Create Cluster wizard.
-
Select Sandbox and click Choose.
-
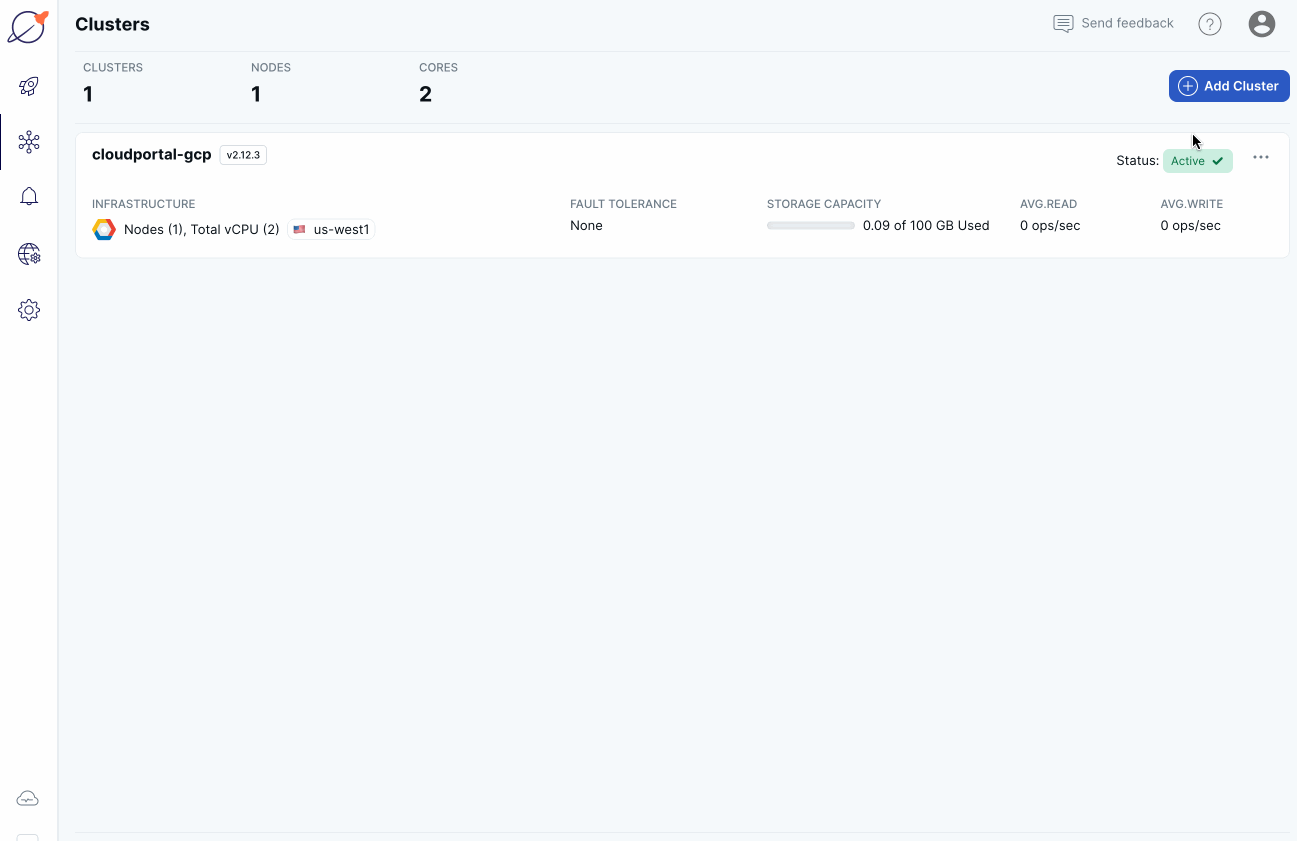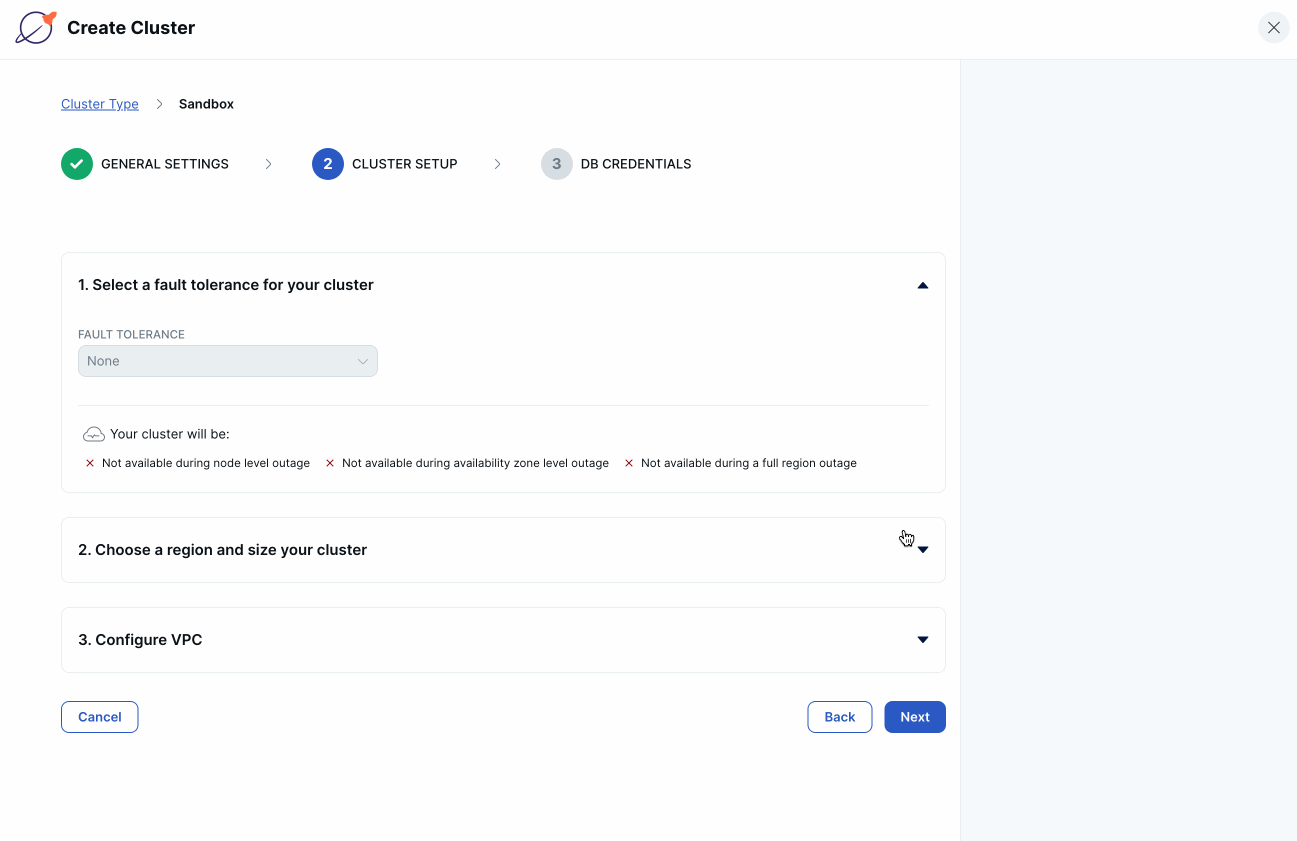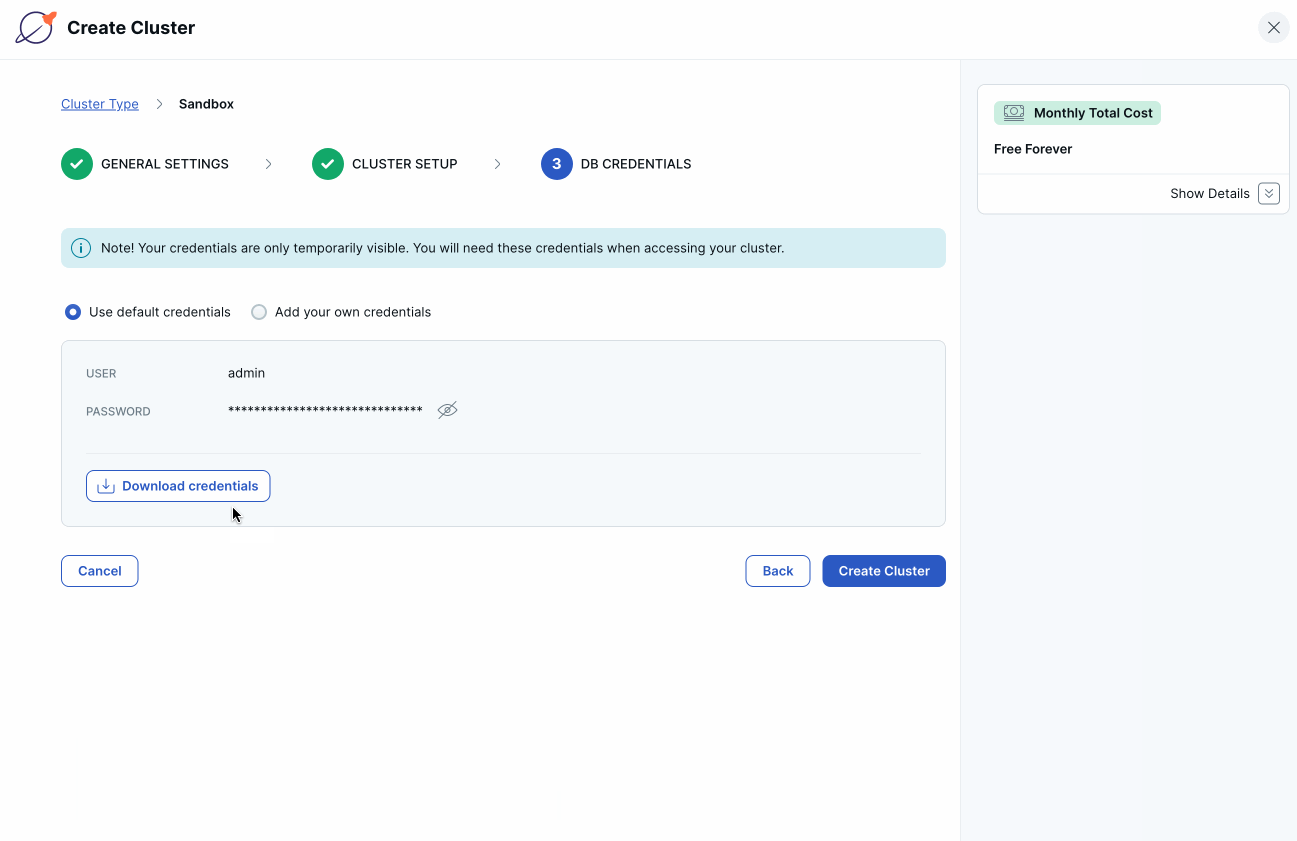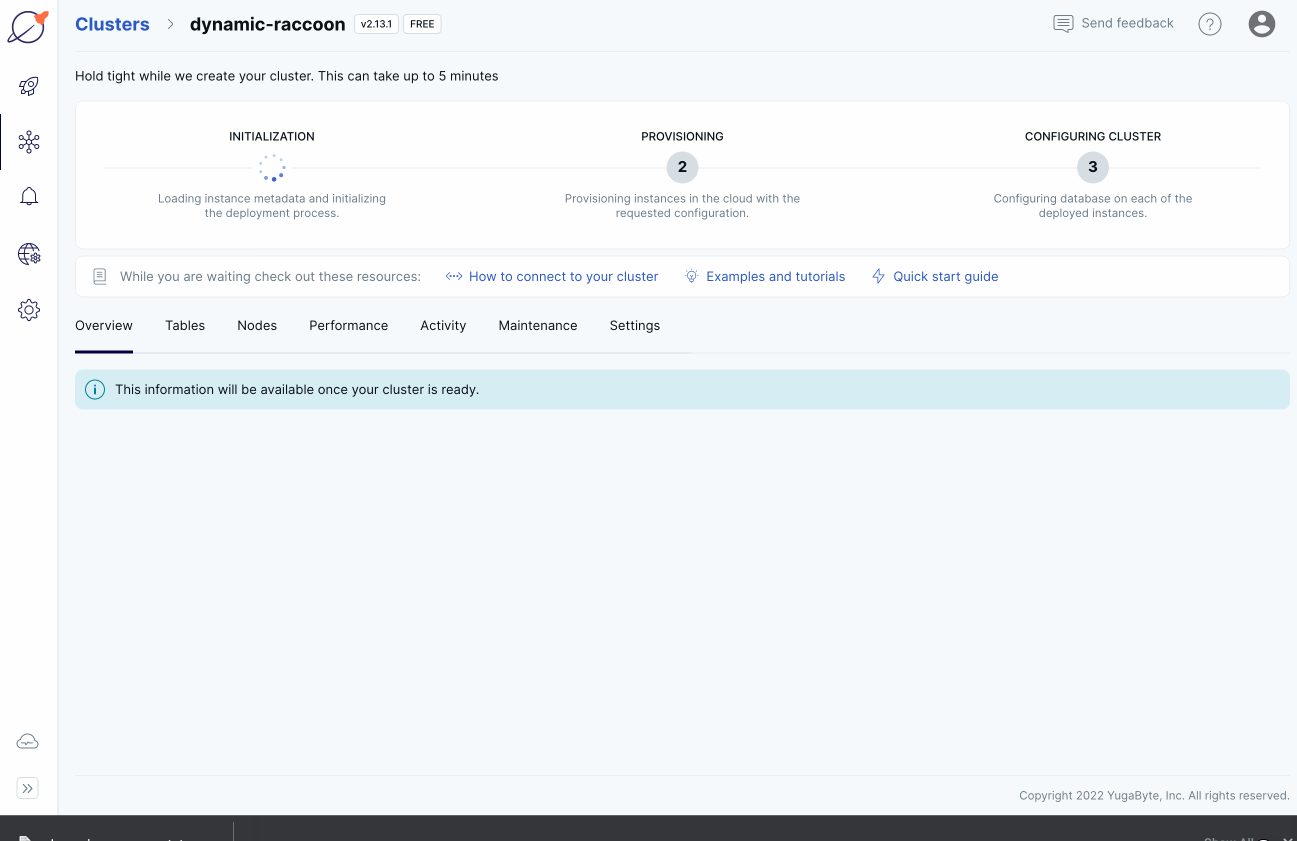
Enter a name for the cluster, and choose the cloud provider (AWS or GCP), then click Next.
-
Choose the region in which to deploy the cluster, then click Next.
-
Click Download credentials. The default credentials are for a database user named "admin". You'll use these credentials when connecting to your YugabyteDB database.
-
Click Create Cluster.
YugabyteDB Managed bootstraps and provisions the cluster, and configures YugabyteDB. The process takes around 5 minutes. While you wait, you can optionally fill out a survey to customize your getting started experience.
When the cluster is ready, the cluster Overview is displayed. You now have a fully configured YugabyteDB cluster provisioned in YugabyteDB Managed.
Sandbox cluster
YugabyteDB is a distributed database optimized for deployment across a cluster of servers. The Sandbox cluster has a single node and limited resources, suitable for running tutorials, Yugabyte University, and building sample applications. See Differences between Sandbox and Dedicated clusters for more information.
To evaluate YugabyteDB Managed for production use or conduct a proof-of-concept (POC), contact Yugabyte Support for trial credits.
Connect to the cluster
Use Cloud Shell to connect to your YugabyteDB Managed cluster from your browser, and interact with it using distributed SQL.
The shell has a one hour connection limit. If your session is idle for more than 5 minutes, it may disconnect. If your session expires, close your browser tab and connect again.
To connect to your cluster, do the following:
-
On the Clusters page, ensure your cluster is selected.
-
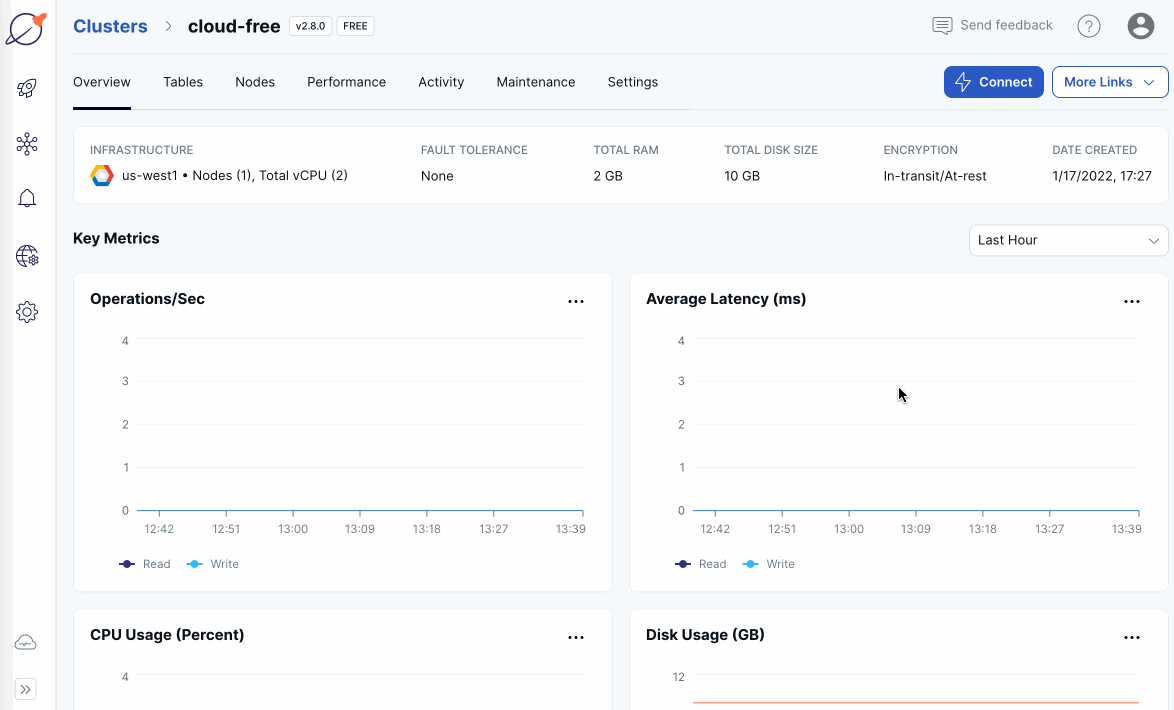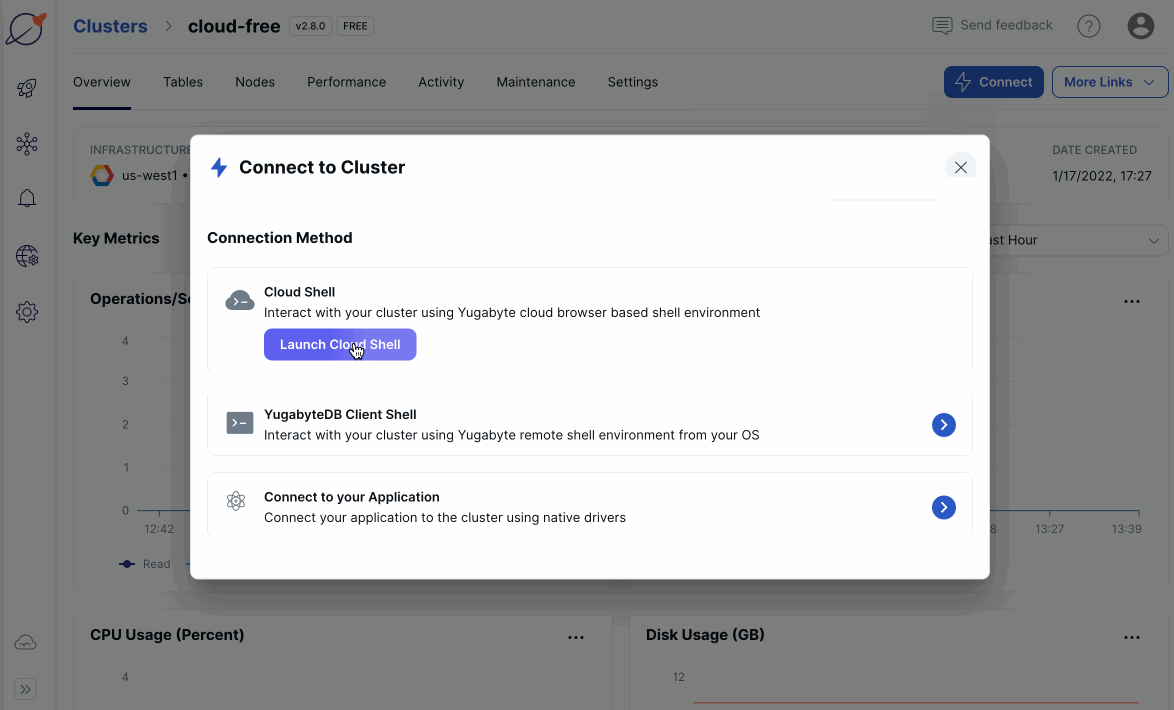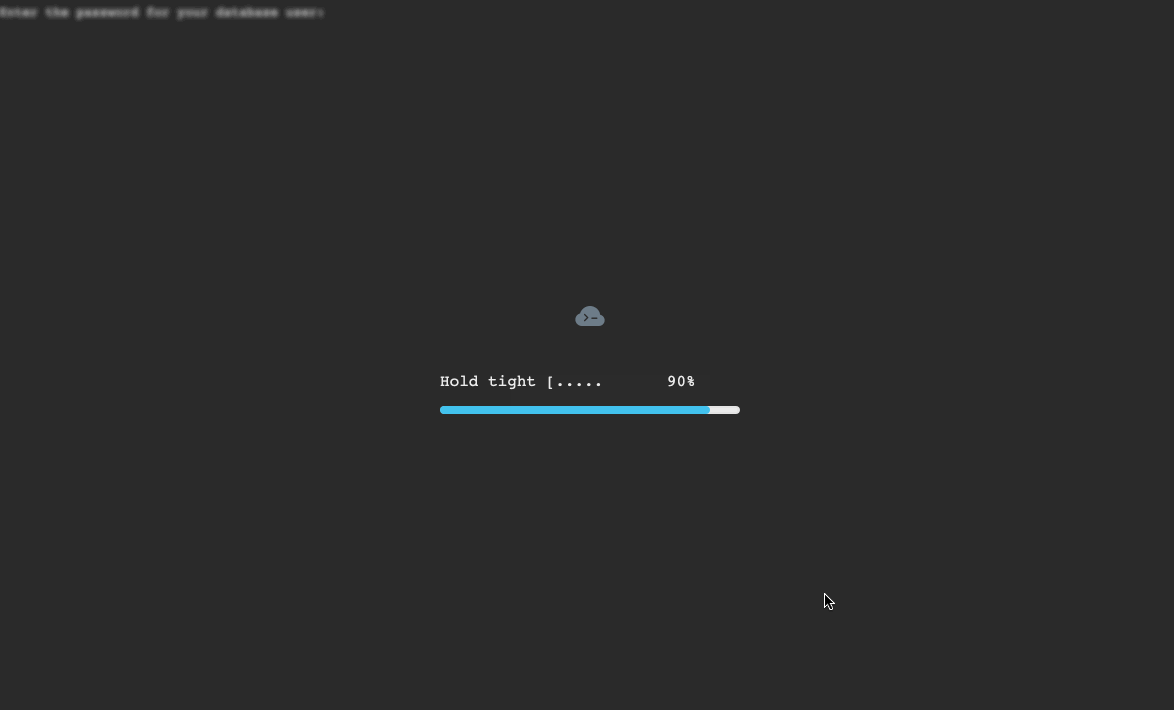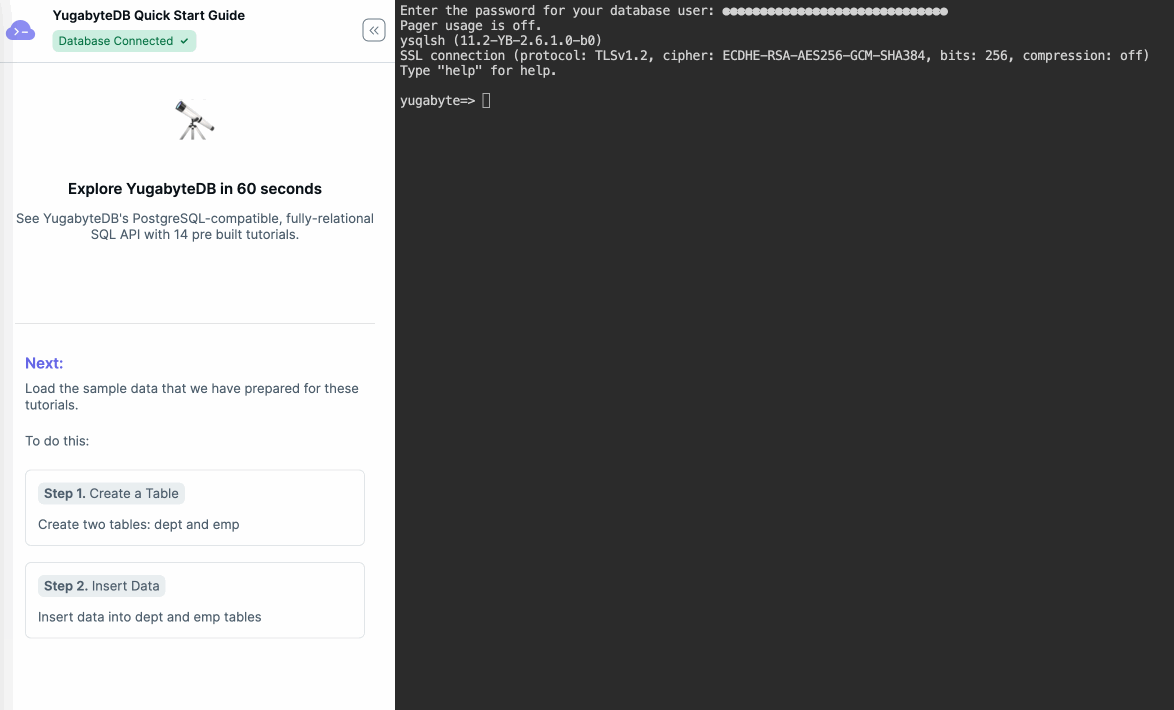
Click Connect to display the Connect to Cluster dialog.
-
Under Cloud Shell, click Launch Cloud Shell.
-
Enter the database name (
yugabyte), the user name (admin), select the YSQL API type, and click Confirm.Cloud Shell opens in a separate browser window. Cloud Shell can take up to 30 seconds to be ready.
Enter your DB password: -
Enter the password for the admin user credentials that you saved when you created the cluster.
The shell prompt appears and is ready to use.ysqlsh (11.2-YB-2.2.0.0-b0) SSL connection (protocol: TLSv1.2, cipher: ECDHE-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384, bits: 256, compression: off) Type "help" for help. yugabyte=> -
When you connect to your cluster using Cloud Shell with the YSQL API (the default), the shell window incorporates a Quick Start Guide, with a series of pre-built queries for you to run. Follow the prompts to explore YugabyteDB in 5 minutes.
The command line interface (CLI) being used is called ysqlsh. ysqlsh is the CLI for interacting with YugabyteDB using the PostgreSQL-compatible YSQL API. Cloud Shell also supports ycqlsh, a CLI for the YCQL API.
For information on other ways to connect to your cluster, refer to Connect to clusters.
Build a Java application
The following tutorial shows a small Java application that connects to a YugabyteDB cluster using the topology-aware Yugabyte JDBC driver and performs basic SQL operations. Use the application as a template to get started with YugabyteDB Managed in Java.
Prerequisites
This tutorial requires the following.
YugabyteDB Managed
- You have a cluster deployed in YugabyteDB Managed.
- You downloaded the cluster CA certificate and added your computer to the cluster IP allow list. Refer to Before you begin.
Other packages
- Java Development Kit (JDK) 1.8, or later, is installed. JDK installers for Linux and macOS can be downloaded from Oracle, Adoptium (OpenJDK), or Azul Systems (OpenJDK). Homebrew users on macOS can install using
brew install openjdk. - Apache Maven 3.3 or later, is installed.
Clone the application from GitHub
Clone the sample application to your computer:
git clone https://github.com/yugabyte/yugabyte-simple-java-app.git && cd yugabyte-simple-java-app
Provide connection parameters
The application needs to establish a connection to the YugabyteDB cluster. To do this:
-
Open the
app.propertiesfile located in the applicationsrc/main/resources/folder. -
Set the following configuration parameters:
- host - the host name of your YugabyteDB cluster. To obtain a YugabyteDB Managed cluster host name, sign in to YugabyteDB Managed, select your cluster on the Clusters page, and click Settings. The host is displayed under Network Access.
- port - the port number that will be used by the JDBC driver (the default YugabyteDB YSQL port is 5433).
- dbUser and dbPassword - the username and password for the YugabyteDB database. If you are using the credentials you created when deploying a cluster in YugabyteDB Managed, these can be found in the credentials file you downloaded.
- sslMode - the SSL mode to use. YugabyteDB Managed requires SSL connections; use
verify-full. - sslRootCert - the full path to the YugabyteDB Managed cluster CA certificate.
-
Save the file.
Build and run the application
First build the application.
$ mvn clean package
Start the application.
$ java -cp target/yugabyte-simple-java-app-1.0-SNAPSHOT.jar SampleApp
If you are running the application on a free or single node cluster, the driver displays a warning that the load balance failed and will fall back to a regular connection.
You should see output similar to the following:
>>>> Successfully connected to YugabyteDB!
>>>> Successfully created DemoAccount table.
>>>> Selecting accounts:
name = Jessica, age = 28, country = USA, balance = 10000
name = John, age = 28, country = Canada, balance = 9000
>>>> Transferred 800 between accounts.
>>>> Selecting accounts:
name = Jessica, age = 28, country = USA, balance = 9200
name = John, age = 28, country = Canada, balance = 9800
You have successfully executed a basic Java application that works with YugabyteDB Managed.
Explore the application logic
Open the SampleApp.java file in the application /src/main/java/ folder to review the methods.
main
The main method establishes a connection with your cluster via the topology-aware Yugabyte JDBC driver.
YBClusterAwareDataSource ds = new YBClusterAwareDataSource();
ds.setUrl("jdbc:yugabytedb://" + settings.getProperty("host") + ":"
+ settings.getProperty("port") + "/yugabyte");
ds.setUser(settings.getProperty("dbUser"));
ds.setPassword(settings.getProperty("dbPassword"));
// Additional SSL-specific settings. See the source code for details.
Connection conn = ds.getConnection();
createDatabase
The createDatabase method uses PostgreSQL-compliant DDL commands to create a sample database.
Statement stmt = conn.createStatement();
stmt.execute("CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS " + TABLE_NAME +
"(" +
"id int PRIMARY KEY," +
"name varchar," +
"age int," +
"country varchar," +
"balance int" +
")");
stmt.execute("INSERT INTO " + TABLE_NAME + " VALUES" +
"(1, 'Jessica', 28, 'USA', 10000)," +
"(2, 'John', 28, 'Canada', 9000)");
selectAccounts
The selectAccounts method queries your distributed data using the SQL SELECT statement.
Statement stmt = conn.createStatement();
ResultSet rs = stmt.executeQuery("SELECT * FROM " + TABLE_NAME);
while (rs.next()) {
System.out.println(String.format("name = %s, age = %s, country = %s, balance = %s",
rs.getString(2), rs.getString(3),
rs.getString(4), rs.getString(5)));
}
transferMoneyBetweenAccounts
The transferMoneyBetweenAccounts method updates your data consistently with distributed transactions.
Statement stmt = conn.createStatement();
try {
stmt.execute(
"BEGIN TRANSACTION;" +
"UPDATE " + TABLE_NAME + " SET balance = balance - " + amount + "" + " WHERE name = 'Jessica';" +
"UPDATE " + TABLE_NAME + " SET balance = balance + " + amount + "" + " WHERE name = 'John';" +
"COMMIT;"
);
} catch (SQLException e) {
if (e.getSQLState().equals("40001")) {
System.err.println("The operation is aborted due to a concurrent transaction that is" +
" modifying the same set of rows. Consider adding retry logic for production-grade applications.");
e.printStackTrace();
} else {
throw e;
}
}