Quick start
Test YugabyteDB's APIs and core features by creating a local cluster on a single host.
The local cluster setup on a single host is intended for development and learning. For production deployment, performance benchmarking, or deploying a true multi-node on multi-host setup, see Deploy YugabyteDB.
Note
The Docker option to run local clusters is recommended only for advanced Docker users. This is because running stateful apps like YugabyteDB in Docker is more complex and error-prone than stateless apps.Install YugabyteDB
Prerequisites
You must have the Docker runtime installed on your localhost. Follow the links below to download and install Docker if you have not done so already.
Install
Pull the YugabyteDB container.
$ docker pull yugabytedb/yugabyte:2.15.0.0-b11
Create a local cluster
To create a 1-node cluster with a replication factor (RF) of 1, run the following command.
$ docker run -d --name yugabyte -p7000:7000 -p9000:9000 -p5433:5433 -p9042:9042\
yugabytedb/yugabyte:latest bin/yugabyted start\
--daemon=false
In the preceding docker run command, the data stored in YugabyteDB doesn't persist across container restarts. To make YugabyteDB persist data across restarts, add a volume mount option to the docker run command.
First, create a ~/yb_data directory:
$ mkdir ~/yb_data
Next, run docker with the volume mount option:
$ docker run -d --name yugabyte \
-p7000:7000 -p9000:9000 -p5433:5433 -p9042:9042 \
-v ~/yb_data:/home/yugabyte/yb_data \
yugabytedb/yugabyte:latest bin/yugabyted start \
--base_dir=/home/yugabyte/yb_data --daemon=false
Clients can now connect to the YSQL and YCQL APIs at localhost:5433 and localhost:9042 respectively.
Check cluster status
$ docker ps
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
5088ca718f70 yugabytedb/yugabyte "bin/yugabyted start…" 46 seconds ago Up 44 seconds 0.0.0.0:5433->5433/tcp, 6379/tcp, 7100/tcp, 0.0.0.0:7000->7000/tcp, 0.0.0.0:9000->9000/tcp, 7200/tcp, 9100/tcp, 10100/tcp, 11000/tcp, 0.0.0.0:9042->9042/tcp, 12000/tcp yugabyte
Check cluster status with Admin UI
Under the hood, the cluster you have just created consists of two processes: YB-Master which keeps track of various metadata (list of tables, users, roles, permissions, and so on), and YB-TServer which is responsible for the actual end user requests for data updates and queries.
Each of the processes exposes its own Admin UI that can be used to check the status of the corresponding process, and perform certain administrative operations. The yb-master Admin UI is available at http://localhost:7000 and the yb-tserver Admin UI is available at http://localhost:9000. To avoid port conflicts, you should make sure other processes on your machine do not have these ports mapped to localhost.
Overview and YB-Master status
The YB-Master home page shows that you have a cluster (or universe) with a replication factor of 1, a single node, and no tables. The YugabyteDB version is also displayed.
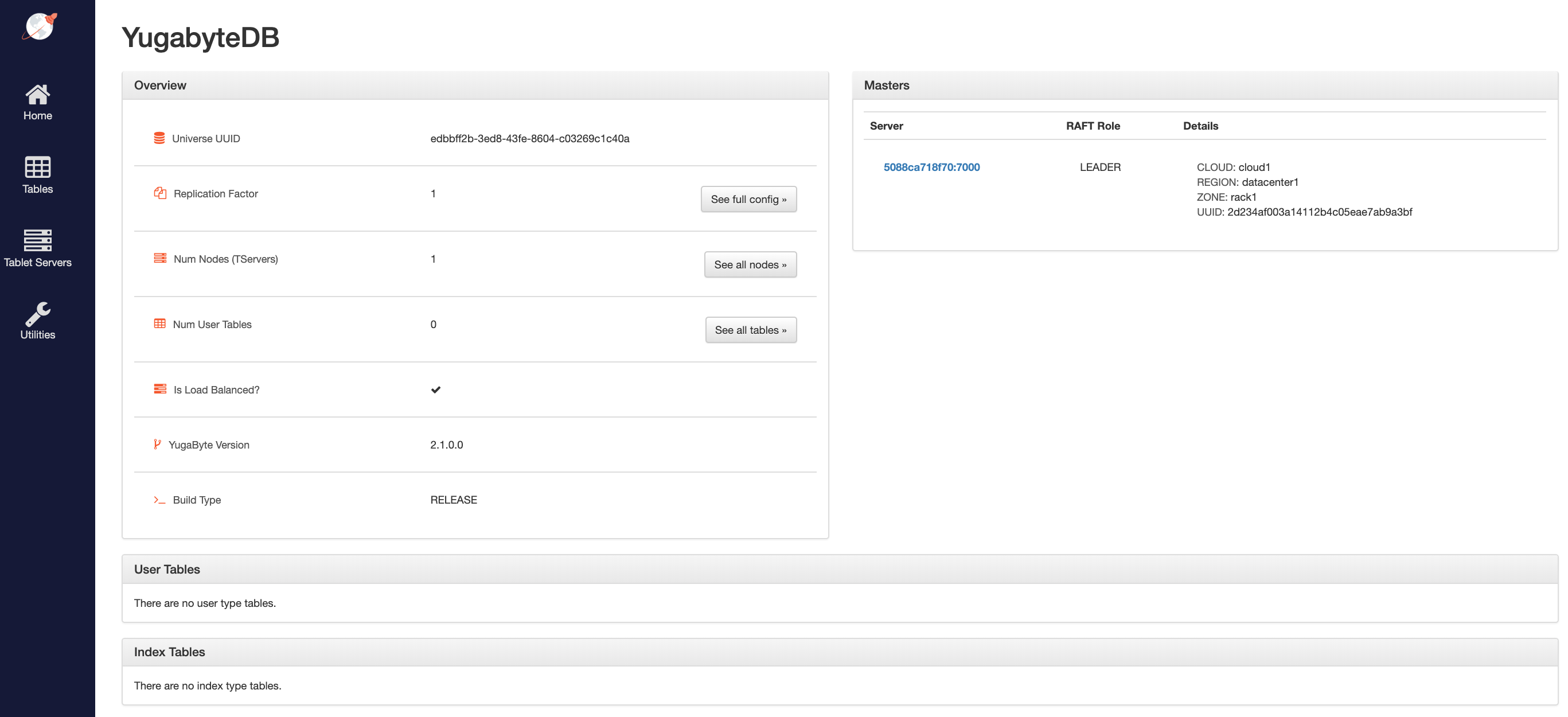
The Masters section highlights the 1 YB-Master along with its corresponding cloud, region, and zone placement.
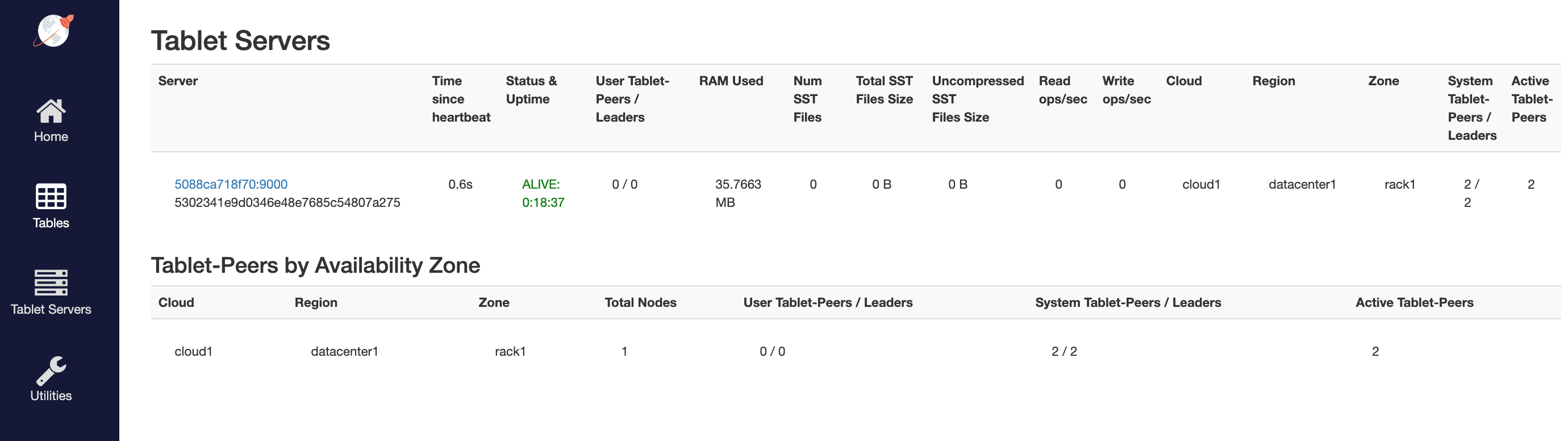
YB-TServer status
Click See all nodes to go to the Tablet Servers page, which lists the YB-TServer along with the time since it last connected to the YB-Master using regular heartbeats.
Build a Java application
Prerequisites
This tutorial assumes that:
-
YugabyteDB is up and running. Using the yb-ctl utility, create a universe with a 3-node RF-3 cluster with some fictitious geo-locations assigned.
$ cd <path-to-yugabytedb-installation> ./bin/yb-ctl create --rf 3 --placement_info "aws.us-west.us-west-2a,aws.us-west.us-west-2a,aws.us-west.us-west-2b" -
Java Development Kit (JDK) 1.8, or later, is installed. JDK installers can be downloaded from OpenJDK.
-
Apache Maven 3.3 or later, is installed.
Create and configure the Java project
-
Create a project called "DriverDemo".
$ mvn archetype:generate \ -DgroupId=com.yugabyte \ -DartifactId=DriverDemo \ -DarchetypeArtifactId=maven-archetype-quickstart \ -DinteractiveMode=false $ cd DriverDemo -
Open the pom.xml file in a text editor and add the following below the
<url>element.<properties> <maven.compiler.source>1.8</maven.compiler.source> <maven.compiler.target>1.8</maven.compiler.target> </properties> -
Add the following dependencies for the driver HikariPool within the
<dependencies>element inpom.xml.<dependency> <groupId>com.yugabyte</groupId> <artifactId>jdbc-yugabytedb</artifactId> <version>42.3.0</version> </dependency> <!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/com.zaxxer/HikariCP --> <dependency> <groupId>com.zaxxer</groupId> <artifactId>HikariCP</artifactId> <version>5.0.0</version> </dependency> -
Save and close
pom.xml. -
Install the added dependency.
$ mvn install
Create the sample Java application
You'll create two java applications, UniformLoadBalance and TopologyAwareLoadBalance. In each, you can create connections in two ways: using the DriverManager.getConnection() API, or using YBClusterAwareDataSource and HikariPool. This example shows both approaches.
Uniform load balancing
-
Create a file called
./src/main/java/com/yugabyte/UniformLoadBalanceApp.java.$ touch ./src/main/java/com/yugabyte/UniformLoadBalanceApp.java -
Paste the following into
UniformLoadBalanceApp.java:package com.yugabyte; import com.zaxxer.hikari.HikariConfig; import com.zaxxer.hikari.HikariDataSource; import java.sql.Connection; import java.sql.DriverManager; import java.sql.SQLException; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; import java.util.Properties; import java.util.Scanner; public class UniformLoadBalanceApp { public static void main(String[] args) { makeConnectionUsingDriverManager(); makeConnectionUsingYbClusterAwareDataSource(); System.out.println("Execution of Uniform Load Balance Java App complete!!"); } public static void makeConnectionUsingDriverManager() { //List to store the connections so that they can be closed at the end List<Connection> connectionList = new ArrayList<>(); System.out.println("Lets create 6 connections using DriverManager"); String yburl = "jdbc:yugabytedb://127.0.0.1:5433/yugabyte?user=yugabyte&password=yugabyte&load-balance=true"; try { for(int i=0; i<6; i++) { Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(yburl); connectionList.add(connection); } System.out.println("You can verify the load balancing by visiting http://<host>:13000/rpcz as discussed before"); System.out.println("Enter a integer to continue once verified:"); int x = new Scanner(System.in).nextInt(); System.out.println("Closing the connections!!"); for(Connection connection : connectionList) { connection.close(); } } catch (SQLException exception) { exception.printStackTrace(); } } public static void makeConnectionUsingYbClusterAwareDataSource() { System.out.println("Now, Lets create 10 connections using YbClusterAwareDataSource and Hikari Pool"); Properties poolProperties = new Properties(); poolProperties.setProperty("dataSourceClassName", "com.yugabyte.ysql.YBClusterAwareDataSource"); //the pool will create 10 connections to the servers poolProperties.setProperty("maximumPoolSize", String.valueOf(10)); poolProperties.setProperty("dataSource.serverName", "127.0.0.1"); poolProperties.setProperty("dataSource.portNumber", "5433"); poolProperties.setProperty("dataSource.databaseName", "yugabyte"); poolProperties.setProperty("dataSource.user", "yugabyte"); poolProperties.setProperty("dataSource.password", "yugabyte"); // If you want to provide additional end points String additionalEndpoints = "127.0.0.2:5433,127.0.0.3:5433"; poolProperties.setProperty("dataSource.additionalEndpoints", additionalEndpoints); HikariConfig config = new HikariConfig(poolProperties); config.validate(); HikariDataSource hikariDataSource = new HikariDataSource(config); System.out.println("Wait for some time for Hikari Pool to setup and create the connections..."); System.out.println("You can verify the load balancing by visiting http://<host>:13000/rpcz as discussed before."); System.out.println("Enter a integer to continue once verified:"); int x = new Scanner(System.in).nextInt(); System.out.println("Closing the Hikari Connection Pool!!"); hikariDataSource.close(); } }Note
When usingDriverManager.getConnection(), you need to include theload-balance=trueproperty in the connection URL. In the case ofYBClusterAwareDataSource, load balancing is enabled by default. -
Run the application.
mvn -q package exec:java -DskipTests -Dexec.mainClass=com.yugabyte.UniformLoadBalanceApp
Topology-aware load balancing
-
Create a file called
./src/main/java/com/yugabyte/TopologyAwareLoadBalanceApp.java.$ touch ./src/main/java/com/yugabyte/TopologyAwareLoadBalanceApp.java -
Paste the following into
TopologyAwareLoadBalanceApp.java:package com.yugabyte; import com.zaxxer.hikari.HikariConfig; import com.zaxxer.hikari.HikariDataSource; import java.sql.Connection; import java.sql.DriverManager; import java.sql.SQLException; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; import java.util.Properties; import java.util.Scanner; public class TopologyAwareLoadBalanceApp { public static void main(String[] args) { makeConnectionUsingDriverManager(); makeConnectionUsingYbClusterAwareDataSource(); System.out.println("Execution of Uniform Load Balance Java App complete!!"); } public static void makeConnectionUsingDriverManager() { //List to store the connections so that they can be closed at the end List<Connection> connectionList = new ArrayList<>(); System.out.println("Lets create 6 connections using DriverManager"); String yburl = "jdbc:yugabytedb://127.0.0.1:5433/yugabyte?user=yugabyte&password=yugabyte&load-balance=true" + "&topology-keys=aws.us-west.us-west-2a"; try { for(int i=0; i<6; i++) { Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(yburl); connectionList.add(connection); } System.out.println("You can verify the load balancing by visiting http://<host>:13000/rpcz as discussed before"); System.out.println("Enter a integer to continue once verified:"); int x = new Scanner(System.in).nextInt(); System.out.println("Closing the connections!!"); for(Connection connection : connectionList) { connection.close(); } } catch (SQLException exception) { exception.printStackTrace(); } } public static void makeConnectionUsingYbClusterAwareDataSource() { System.out.println("Now, Lets create 10 connections using YbClusterAwareDataSource and Hikari Pool"); Properties poolProperties = new Properties(); poolProperties.setProperty("dataSourceClassName", "com.yugabyte.ysql.YBClusterAwareDataSource"); //the pool will create 10 connections to the servers poolProperties.setProperty("maximumPoolSize", String.valueOf(10)); poolProperties.setProperty("dataSource.serverName", "127.0.0.1"); poolProperties.setProperty("dataSource.portNumber", "5433"); poolProperties.setProperty("dataSource.databaseName", "yugabyte"); poolProperties.setProperty("dataSource.user", "yugabyte"); poolProperties.setProperty("dataSource.password", "yugabyte"); // If you want to provide additional end points String additionalEndpoints = "127.0.0.2:5433,127.0.0.3:5433"; poolProperties.setProperty("dataSource.additionalEndpoints", additionalEndpoints); // If you want to load balance between specific geo locations using topology keys String geoLocations = "aws.us-west.us-west-2a"; poolProperties.setProperty("dataSource.topologyKeys", geoLocations); HikariConfig config = new HikariConfig(poolProperties); config.validate(); HikariDataSource hikariDataSource = new HikariDataSource(config); System.out.println("Wait for some time for Hikari Pool to setup and create the connections..."); System.out.println("You can verify the load balancing by visiting http://<host>:13000/rpcz as discussed before."); System.out.println("Enter a integer to continue once verified:"); int x = new Scanner(System.in).nextInt(); System.out.println("Closing the Hikari Connection Pool!!"); hikariDataSource.close(); } }Note
When usingDriverManager.getConnection(), you need to include theload-balance=trueproperty in the connection URL. In the case ofYBClusterAwareDataSource, load balancing is enabled by default, but you must set propertydataSource.topologyKeys. -
Run the application.
mvn -q package exec:java -DskipTests -Dexec.mainClass=com.yugabyte.TopologyAwareLoadBalanceApp